India Fertilizer Market and Volume Forecast Report (2025–2033)
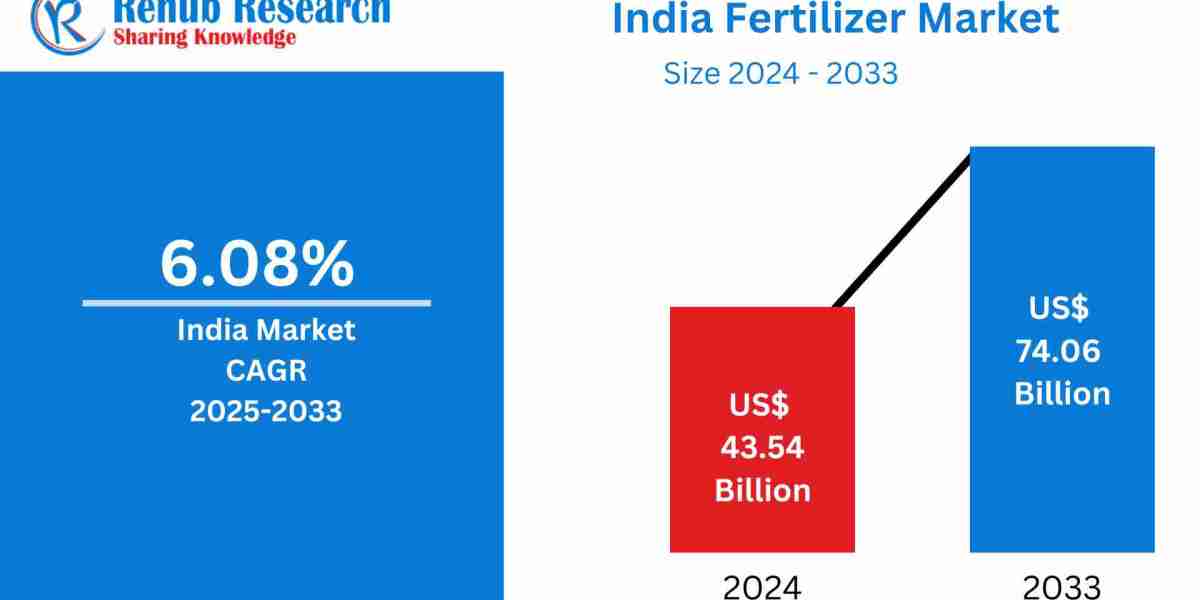
Market Overview The India Fertilizer Market is projected to grow from US$ 43.54 billion in 2024 to US$ 74.06 billion by 2033, reflecting a CAGR of 6.08% during the forecast period. The growth is attributed to increasing agricultural productivity, government subsidies, and rising demand for crops such as wheat, rice, and vegetables. Additionally, a growing emphasis on sustainable agricultural practices, including balanced nutrient management and bio-fertilizer adoption, is reshaping the market landscape.
Market Definition and Outlook Fertilizers are chemical or natural substances used to enhance soil fertility and plant growth. In India, fertilizers play a pivotal role in boosting the productivity of staple crops, including rice, wheat, sugarcane, and vegetables. With a significant portion of the rural economy dependent on agriculture, fertilizers are subsidized by the Indian government to ensure affordability and food security. The focus on innovative and sustainable farming methods, including the adoption of bio-fertilizers and reduced chemical dependency, is rising in response to environmental challenges and soil degradation.
Key Market Drivers
1. Government Subsidies and Support The Indian government has implemented multiple initiatives to support the fertilizer industry. These include direct subsidies on urea, DAP, and NPK, making fertilizers affordable and accessible. Notable schemes include:
o Nutrient-Based Subsidy (NBS) Scheme: Companies fix the MRP based on market dynamics while the government monitors prices.
o PM-PRANAM Scheme: Offers grants to states/UTs saving chemical fertilizer usage.
o Special DAP Subsidy: ₹3500/MT allocated from April to December 2024.
o Encouragement for nano fertilizers like Nano Urea and Nano DAP.
2. Rising Agricultural Demand India’s rapidly growing population—expected to hit 1.7 billion by 2064—necessitates a sharp increase in agricultural output. Fertilizers help meet this demand by enhancing soil nutrient content and supporting higher yields, especially in high-demand regions like Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, and Maharashtra.
3. Sustainable Farming Trends Growing awareness of environmental degradation has driven interest in sustainable agriculture. Bio-fertilizers, micronutrients, and organic alternatives are gaining traction, encouraged by both government policy and increasing farmer awareness.
Key Market Challenges
1. Excessive Chemical Usage Over-reliance on nitrogen-based fertilizers like urea leads to soil degradation, reduced fertility, and water pollution. There's an urgent need for balanced nutrient application and the promotion of eco-friendly alternatives.
2. High Prices and Availability Issues Despite subsidies, raw material costs and global price volatility affect fertilizer affordability. Distribution issues in remote regions further impede timely fertilizer application.
Fertilizer Segment Analysis
· Urea Fertilizers: Most widely used, supported by government subsidies, essential for nitrogen supply.
· DAP Fertilizers: Popular for phosphorus content, high demand during Rabi season, heavily import-dependent.
· MOP Fertilizers: Key for potassium needs; entirely import-based with major use in Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu.
· Complex Fertilizers: Custom blends tailored to regional crop needs; gaining traction for balanced nutrition.
Sectoral Analysis
· Public Sector: Companies like RCF and NFL ensure rural fertilizer availability but face efficiency and infrastructure challenges.
· Cooperative Sector: Strong rural networks offer subsidized access and support to marginal farmers.
· Private Sector: Led by companies such as Coromandel and Chambal; focus on innovation, precision farming, and specialty fertilizers.
State-Level Market Analysis
· Uttar Pradesh: Fastest-growing state with vast farmland and large fertilizer demand; 4.8 MT stock developed for kharif 2024.
· Punjab: Highest per-hectare fertilizer consumption (223 kg); facing sustainability challenges.
· Andhra Pradesh: Focus on rice, maize, and pulses; shift towards organic practices encouraged.
Recent Developments and Initiatives
· July 2024: GOI mandates Nano Urea and Nano DAP standards; boosts production at NFL and RCF.
· April 2023: IFFCO launches Nano DAP Liquid Fertilizer to support sustainable farming.
· December 2023: Rallis India launches NAYAZINC™, a patented zinc fertilizer.
· September 2023: Coromandel International releases Cumist Calcium to improve soil health.
· August 2023: Gujarat CM inaugurates drone-based nano urea spraying initiative.
Key Companies Profiled
· Coromandel International Ltd
· Rashtriya Chemicals & Fertilizers Ltd (RCF)
· National Fertilizers Ltd (NFL)
· Chambal Fertilisers & Chemicals Ltd
· Nagarjuna Fertilizers and Chemicals Ltd
Market Segmentation
By Fertilizer Type
1. Urea
2. DAP
3. MOP
4. Complex Fertilizers
By Sector
1. Public
2. Cooperative
3. Private
By State
· Andhra Pradesh
· Bihar
· Chhattisgarh
· Gujarat
· Haryana
· Jammu and Kashmir
· Jharkhand
· Karnataka
· Kerala
· Madhya Pradesh
· Maharashtra
· Odisha
· Puducherry
· Punjab
· Rajasthan
· Tamil Nadu
· Telangana
· Uttar Pradesh
· Uttarakhand
· West Bengal
Conclusion The India Fertilizer Market is undergoing significant transformation, propelled by government support, population growth, and the push toward sustainable agriculture. Despite challenges like soil degradation and rising input costs, opportunities lie in innovation, balanced fertilization, and public-private cooperation. Strategic initiatives and modernization are expected to shape a robust fertilizer ecosystem through 2033.